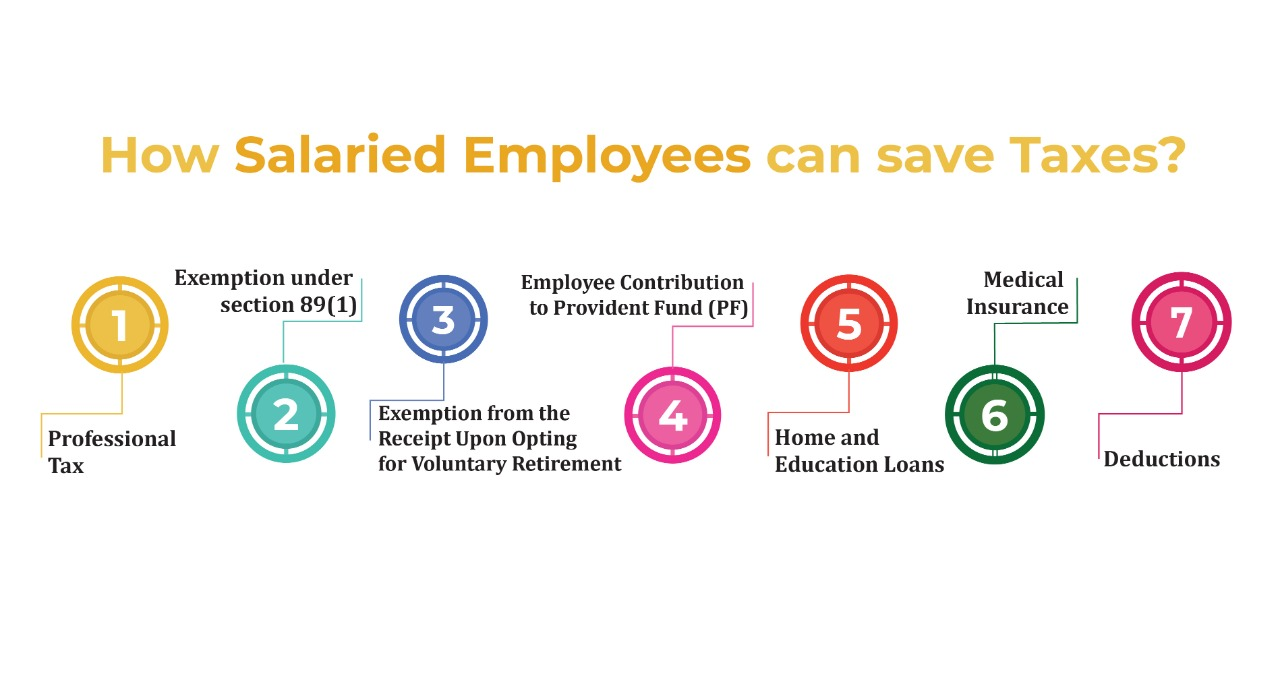
IT Assets are often neglected as they fall in between the long term fixed assets and short term inventory in terms of durability.
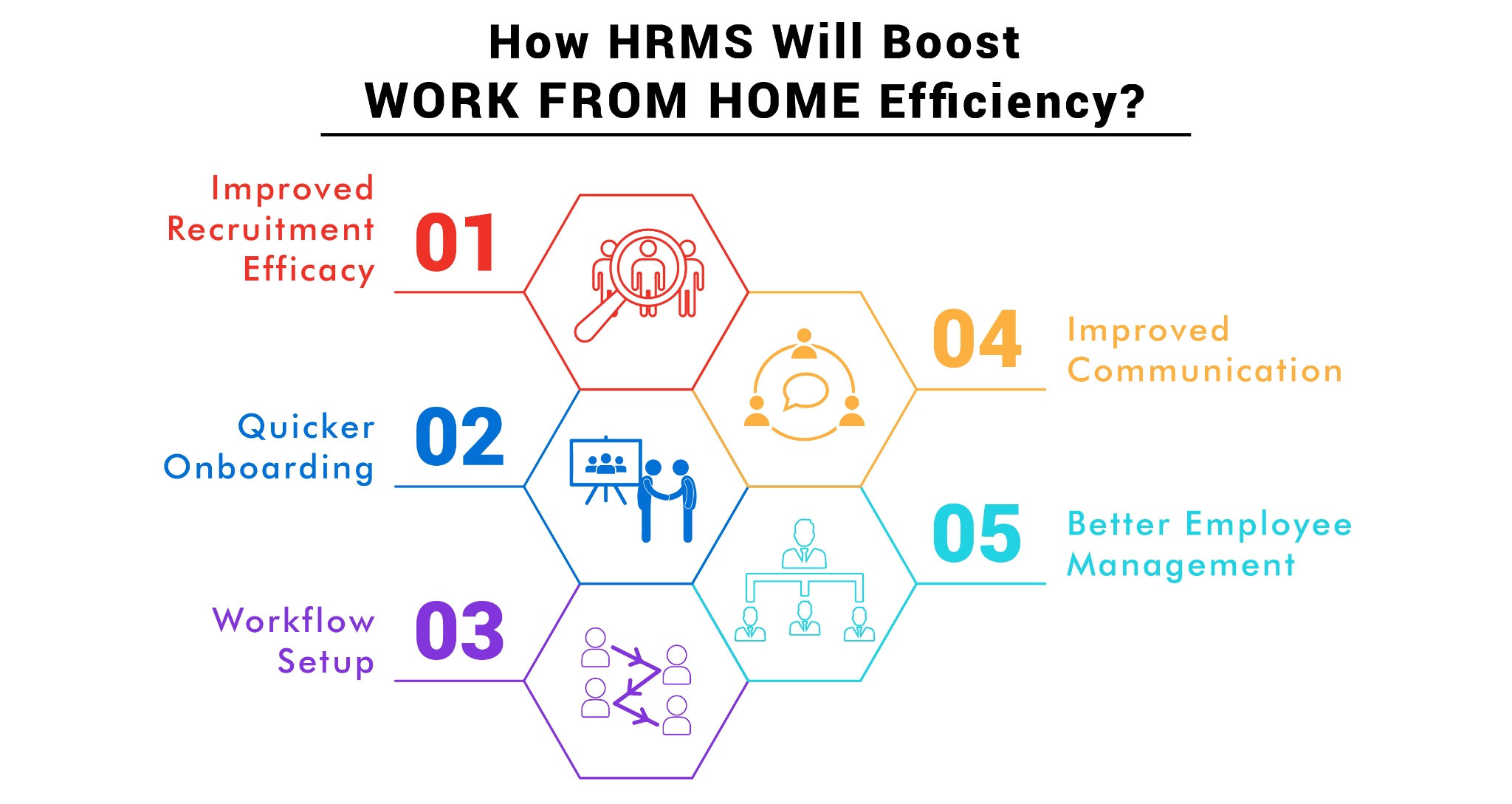
If looked at from a different perspective, IT Assets are the core of an organisation. Be it laptops, desktops or just anti-virus software, IT Assets need to be tracked and managed like actual fixed assets. Here are 4 ways in which a Good FAMS will help you manage your IT Assets:
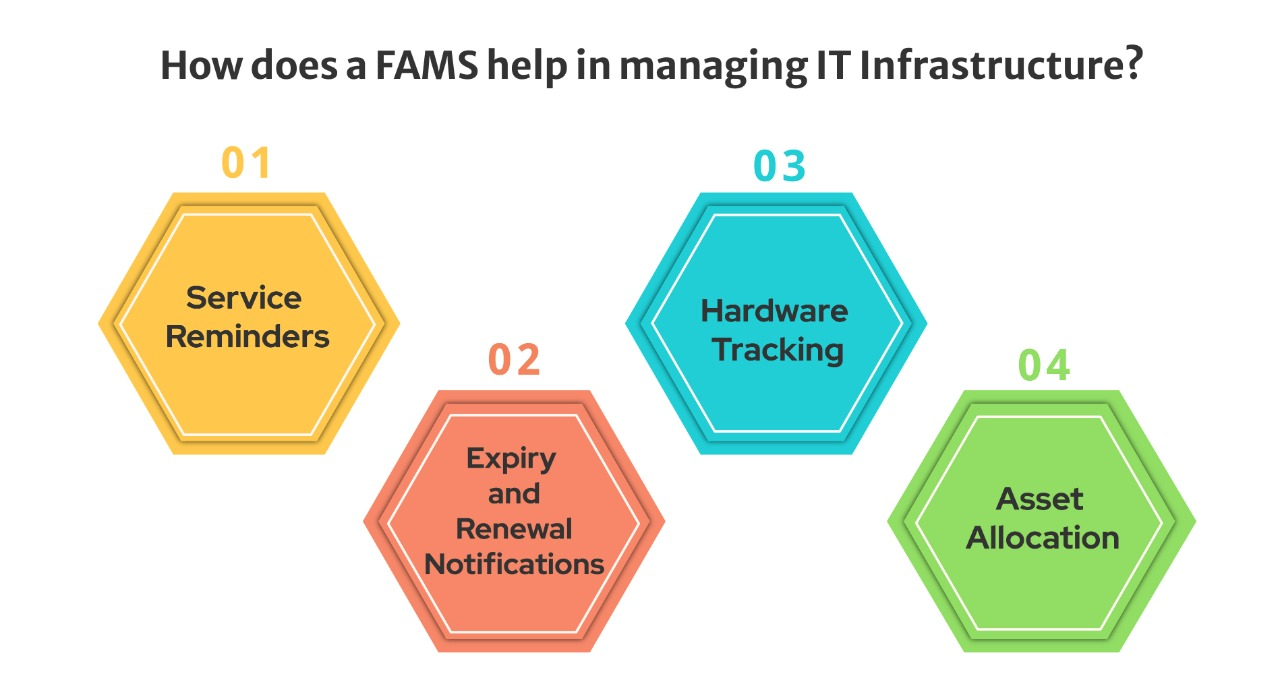
– Service Reminders
The IT Admins all collectively might agree on one thing that maintaining a date sheet to track IT Hardware is one hectic job. What if this tedious task was performed by a software/ system? A Fixed Asset Management System ensures that you never miss out on any of your asset services due. Get automated reminders for whenever your IT infrastructure like laptops, desktops, biometric systems, etc call for service. No more stress to the IT Admin with Email and pop-up reminders for every asset to the Admin as well as the employee the asset has been allocated to!
– Expiry and Renewal Notifications
It is one thing to keep a track of hardware service due and another thing to ensure that all the softwares is up to date, running and the respective certificates are not expired. SSL and SQL Certificates also need to be renewed. With a Fixed Assets Management System, the IT Admin can focus on other important tasks while the system tracks the expiry and renewal of such software and encryption certificates.

– Hardware Tracking
“Which asset is allocated to which employee in which department?” Now that is something you will not need to worry about with a Fixed Assets Management Software. You can generate and allocate a barcode to each and every IT Asset and track it. You can issue the barcode for every change in asset and the employee allocated to have an accurate track of the asset. This saves time as one can know which employee the particular tech is allotted to by just scanning the code. Not only that, one can also know the department of the employee and the period for which the asset is issued.
– Asset Allocation
Talking of allocation, Asset Allocation is another major reason you should consider getting a Fixed Asset Management System. Allocating assets with proper barcodes/ QR Codes/ RFID Tags allows you to accurately track assets, more importantly IT Assets which tend to move more frequently in an organisation. Allocation of assets also helps in making the workflow easier by ensuring that the proper employee has the proper asset.
In short, A FAMS helps an organisation manage it’s IT Infrastructure by keeping a date sheet and reminding and/or notifying about renewals/ expiry/ service dues, by Helping them track the IT Assets and by assisting in allocating the proper asset to the proper employee.
If you are looking for a FAMS which excels in the above mentioned necessities, you should consider Spine Assets. Spine Assets not only covers the 4 basic necessities but also offers many more features that will help your organisation boost its asset management efficiency.


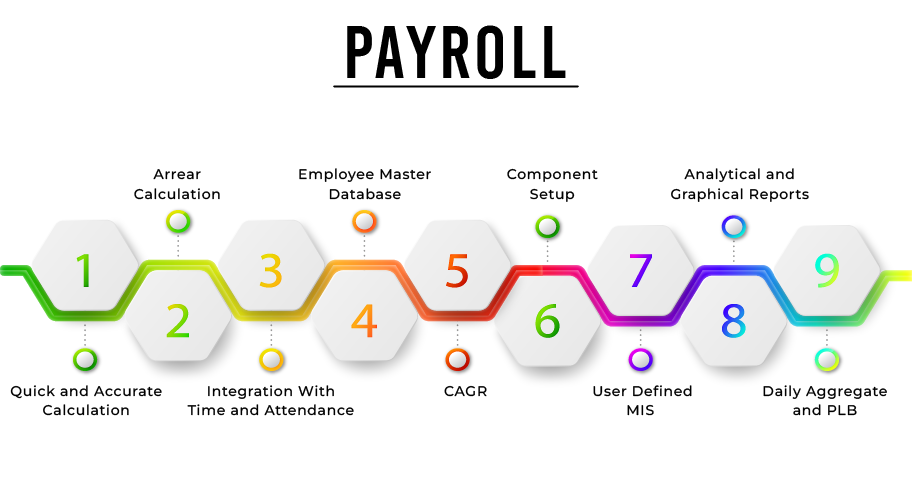 1.Quick and Accurate Calculation
1.Quick and Accurate Calculation