What is an “End to End” HR Solution you might ask.
An End to End HR Solution refers to an HR System which records and tracks the data of employees since the very beginning or onboarding or since they were hired. It keeps recording the data of the particular employee till the day of his/her exit.
Now that we have a basic idea of what an “end to end” solution refers to, let us learn why is it necessary?
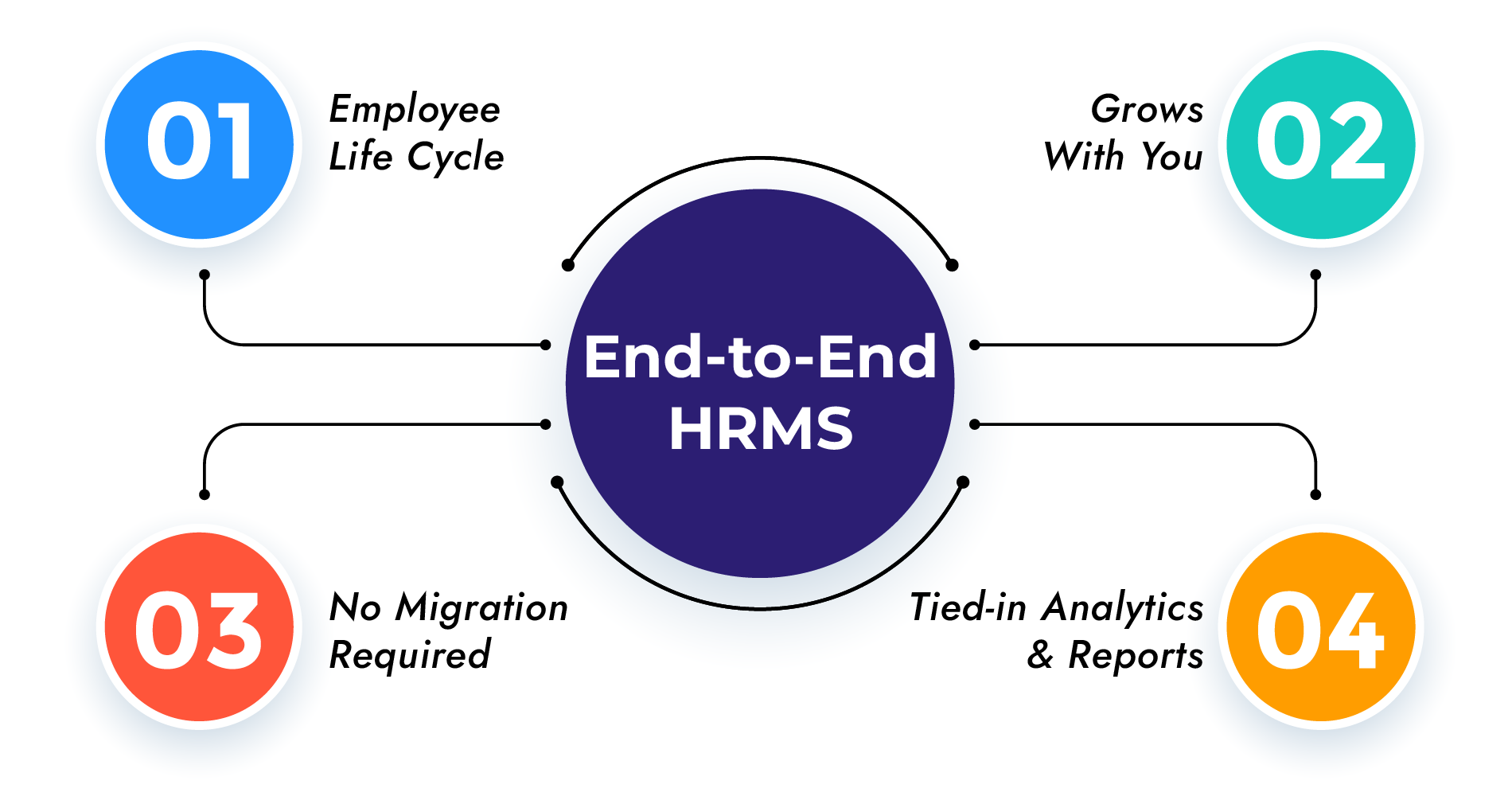
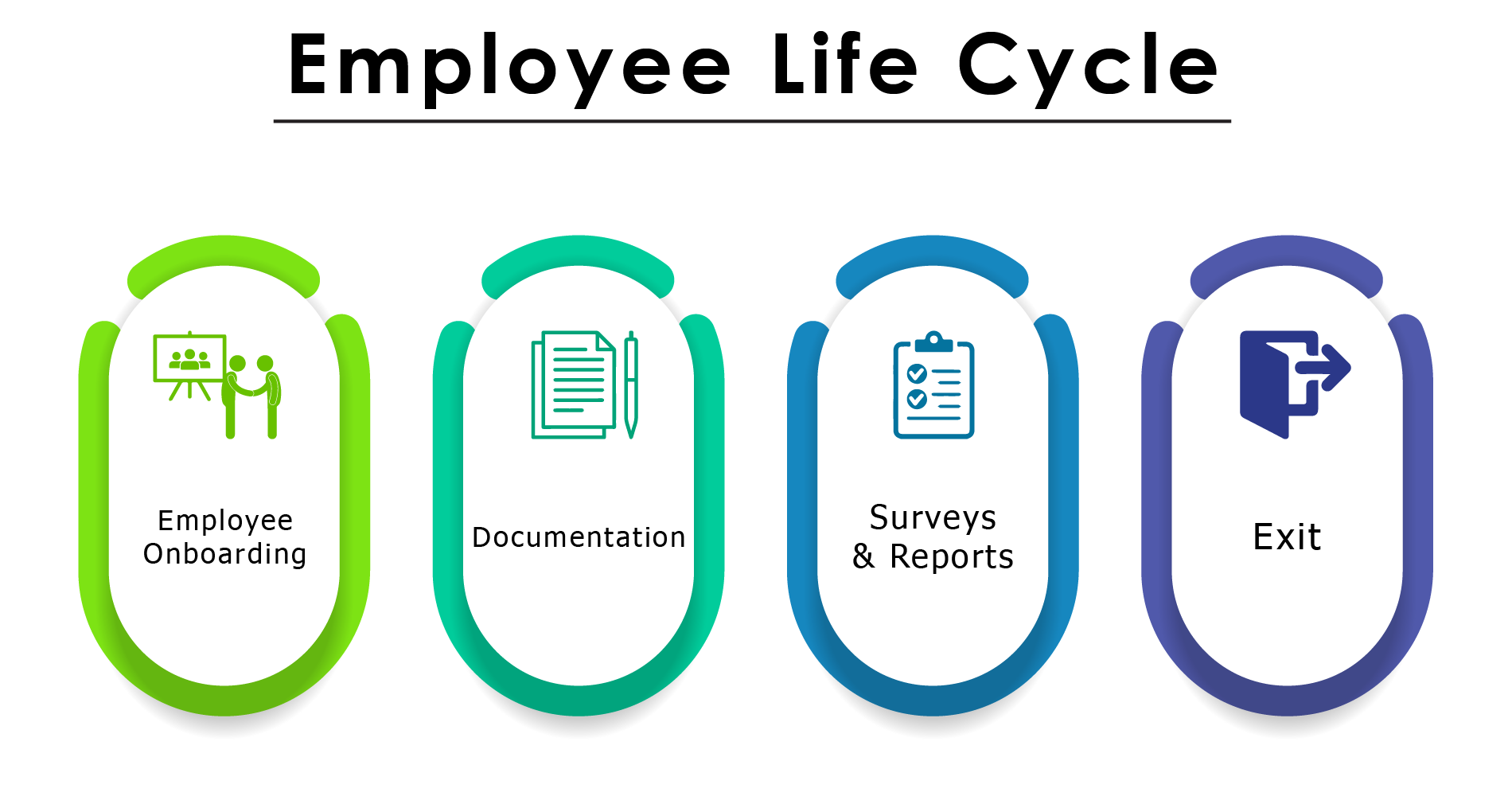
– Employee Life Cycle
“Onboarding to exit”, “Hire to retire” whatever you want to call it. Employee Life Cycle is the period for which an employee works at a particular organisation. It also includes the onboarding and exit processes. From the moment of onboarding till the full and final settlement is done and the money is received/paid by the employee, the Employee Life Cycle goes on. From onboarding to exit, an end-to-end HRMS ensures the employee has no obstacles in communication with the employer. It also provides the required reports to the employer whenever required. For more information on ELC you can read What does Employee Life Cycle mean and how does an HRMS affect it?
– Grows With You
A Human Resource Management System, Being modular and flexible, grows as you do! Needless to say, having modularity makes an HRM system segment agnostic and boosts the compatibility of the system. You can add modules and make the system even more comprehensive as you grow as an organisation. If you would like to know more about scalability in HRMS, you can read How is a scalable HRMS better for your organisation?

– No Migration Required
Say you have to switch to a new solution provider just because you now have a huge force of employees and the solution provider does not have the adequate tech to manage so many employees. The amount of work and expenses incurred in the migration process would be overwhelming. What if you just had to update the system once? With Spine HR Suite, you can upgrade the system instead of migrating to a whole new system which cuts down your migration costs and boosts the data retention efficiency.
– Tied-in Analytics & Reports
An end-to-end/ Hire to Retire/ Onboarding to Exit or whatever you want to call it solution, stores the data of your organisation since the deployment of the system. The amount of reports you can generate when required, the depth of reports and the accuracy is unimaginable. When you have an End to End HR Management system deployed, you could care less about reports and analytics it provides.
To sum it up, End to End Human Resource Solutions are the way to go! You get numerous benefits which include cutting down migration and upgradation costs, bulk purchasing costs, report extraction costs and on the other hand you get the whole life cycle of your employee at a glance, extremely detailed and accurate reports (filtered, sorted and created according to your requirements) and much much more!
If you are looking for one such HRMS which would counter all your hR requirements, Spine HR Suite is the way to go! Click here to learn more about Spine HR Suite.


 \
\

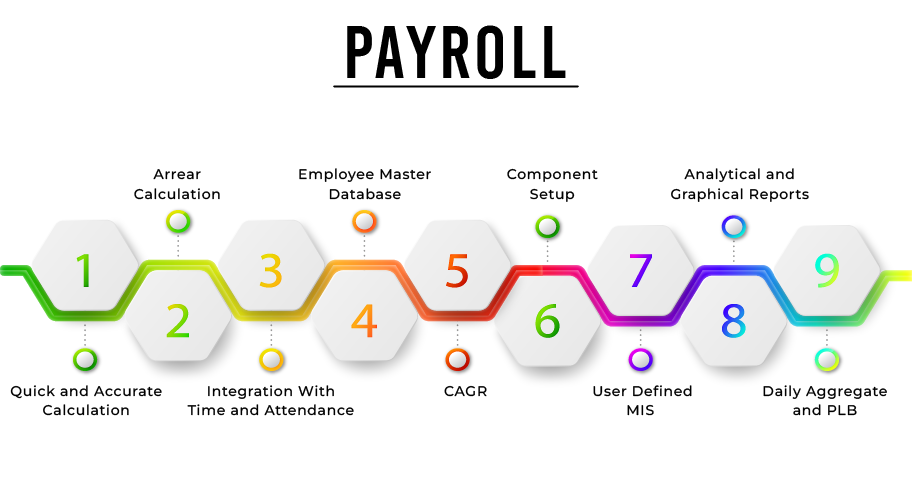 1.Quick and Accurate Calculation
1.Quick and Accurate Calculation